Background
The U.S. energy sector is in the midst of transformational change. Emerging technologies and societal demand promise to reshape not only the energy we use, but also how we use it.
Our regulatory environment and approval process must incorporate a “common sense” approach, helping streamline project approvals while encouraging innovative approaches to upgrade our energy and utility infrastructure.
We must integrate renewable energy, energy storage, and other emerging technologies into a cohesive energy portfolio in order to meet tomorrow’s energy demands, today.
The Challenge
There are a number of issues facing our nation’s energy infrastructure. From the source of energy – fossil fuels or renewables – to storage and distribution of power; threats, shortfalls, and challenges appear on all fronts.
As climate increasingly takes center stage, we are witnessing a shift from traditional fossil fuel and carbon-intensive power generation to greener alternatives and renewables. These face issues like diluteness and intermittency, which requires some type of power storage infrastructure. The market for solar, wind, hydroelectric, and other renewables is not as competitive as traditional resources and often have subsidies and government disruptions to market equilibria.
Our electrical grids lack the intelligence that other systems in our infrastructure are integrating. Features allowing power to be measured, routed, and diverted from numerous sources and with dynamic responsiveness to realtime demand are the future. Additionally, the security of our grid is in jeopardy. National intelligence officials believe hostile foreign powers could remotely disrupt power plants or that an electromagnetic attack could take them all offline.
These and more represent both technical and regulatory hurdles we must overcome to improve efficiency, safety, and resilience in our energy infrastructure.
The Solution
Research and development are critical to any technical challenge. But without the regulatory pieces falling into place as well, we can get nowhere. We must have a regulatory climate that encourages innovation and investment, that also balances costs and benefits.
Before our energy sector and infrastructure can transition to all green processes, significant advances in power storage are essential. Whether that is new batteries, more efficient allocation networks, or something unimagined thus far, we cannot realistically rely on the free resources of sun and wind without that next innovation.
A smarter grid is also needed. And this comes from both the technical side and regulatory side of the equation.
Featured Works Below
Policy Blog
Policy Briefs and White Papers
Cover Title Published Keywords Download hf:doc_categories hf:doc_tags 
Broadening Our View on Broadband: Identifying additional benefits from current fiber and future build outs that generate more economic growth and help reduce harm May, 2025 Energy, Innovation and Technology, Economics, Grid white-papers energy innovation-and-technology economics grid 
Looming energy security risks: Emerging demand-led vulnerabilities to energy infrastructure May, 2025 Energy, Innovation and Technology, Economics, Grid white-papers energy innovation-and-technology economics grid 
Beyond Broadband: Tapping the Multi-Use Advantages of Nationwide Fiber Optic Infrastructure May, 2025 Transportation, Energy, Innovation and Technology, Economics policy-briefs transportation energy innovation-and-technology economics 
Achieving American Energy, Infrastructure, and Economic Wins Simultaneously: Leveraging policy to scale private sector innovation for nationwide impact May, 2025 Transportation, Energy, Innovation and Technology policy-briefs transportation energy innovation-and-technology 
Maximizing The Potential of 45Q: Untapped opportunities in existing carbon capture incentives February, 2025 Decarbonization, Energy, Innovation and Technology, Climate and Conservation policy-briefs decarbonization energy innovation-and-technology climate-and-conservation 
The Hydrogen Highway: How distributed hydrogen production can maximize existing infrastructure, avoid costs and complications, and jumpstart national hydrogen demand November, 2024 Transportation, Decarbonization, Energy, Hydrogen white-papers transportation decarbonization energy hydrogen 
America’s Backbone: The Importance of Steel and its Evolving Demand September, 2024 Energy, Economics, Steel white-papers energy economics steel 
Geothermal Energy Brief August, 2024 Energy policy-briefs energy 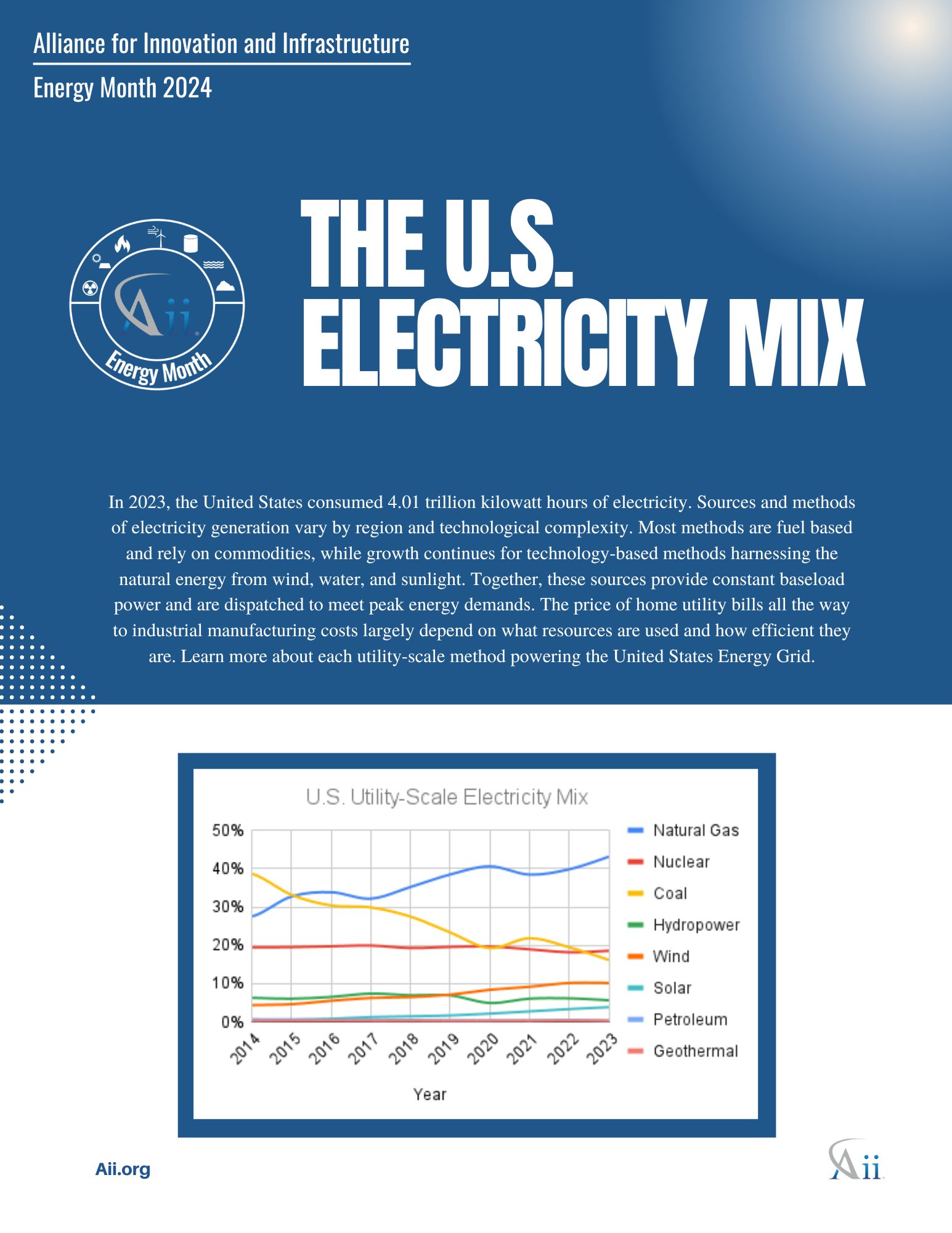
2024 Energy Spotlights: The U.S. Electricity Mix July, 2024 Energy, Climate and Conservation, Grid policy-briefs energy climate-and-conservation grid 
Building New Critical Infrastructure: No Time to Waste. Evaluating Cost Transparency Between a Federal Right of First Refusal and Competitive Bidding in Electrical Transmission Infrastructure Expansion July, 2024 Energy, Economics, Transmission, Grid white-papers energy economics transmission grid 
A Unique Win-Win: Bolstering Texas’ Energy Security by Leveraging Existing Infrastructure to Effectively Decarbonize June, 2024 Decarbonization, Energy, Innovation and Technology, Climate and Conservation white-papers decarbonization energy innovation-and-technology climate-and-conservation 
Improving Upon Our Dig Laws: Framing Out a Plan For Achieving a 50 Percent Reduction in Excavation Damage December, 2023 Damage Prevention, Energy, Public Safety white-papers damage-prevention energy public-safety 
Unseen Threats to Texas Critical Infrastructure: The Risk to Buried Utilities and Targeted Policy Solutions to Protect Them October, 2023 Damage Prevention, Energy, Public Safety white-papers damage-prevention energy public-safety 
Pathways to Decarbonizing Heat: Building a Holistic Framework for Evaluating and Ranking Decarbonization Strategies for Industrial Heat in Light of Economic Efficiency, Public Policy, Timing Readiness, and Infrastructure Realities September, 2023 Decarbonization, Energy, Innovation and Technology, Climate and Conservation white-papers decarbonization energy innovation-and-technology climate-and-conservation 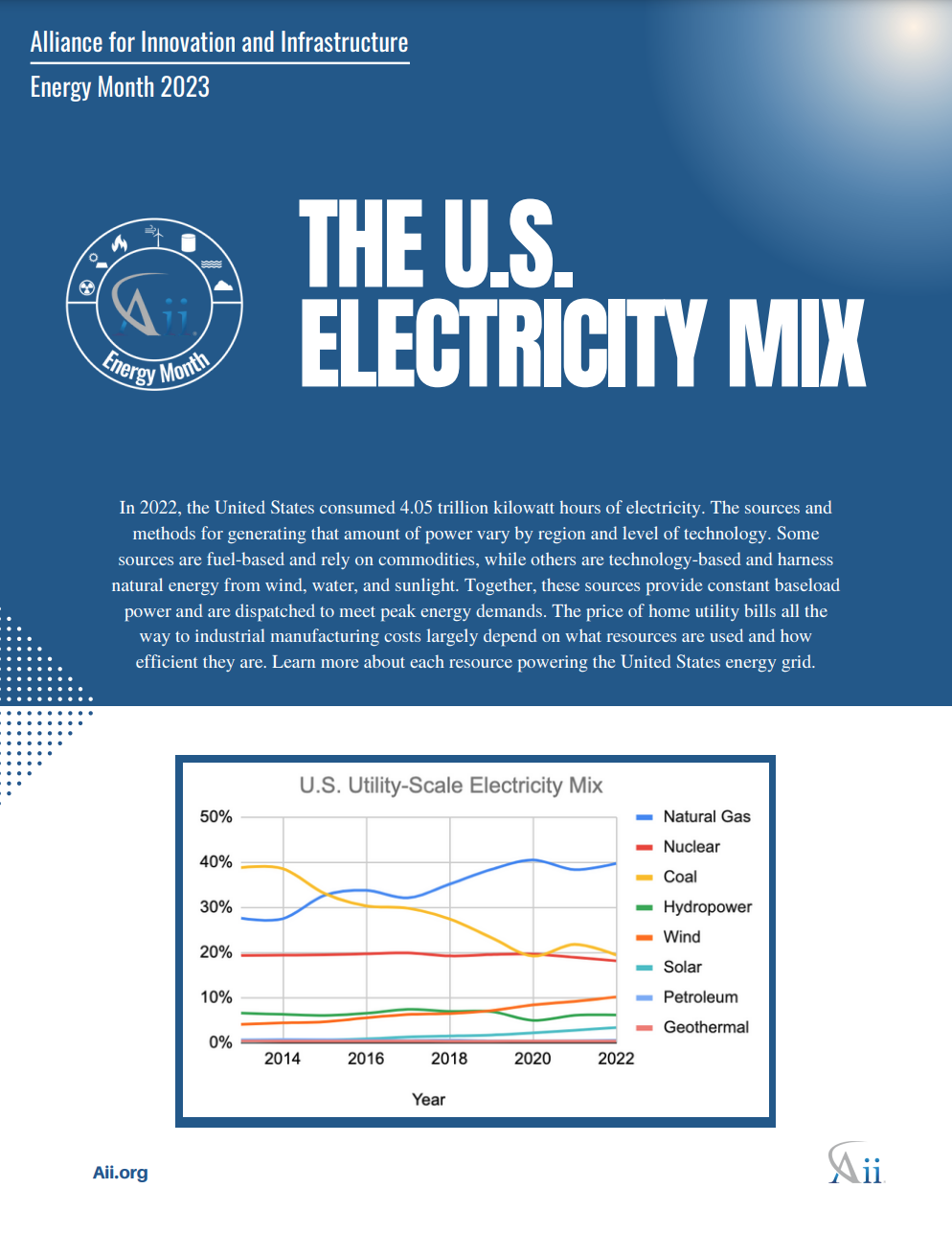
The U.S. Electricity Mix: 2023 Energy Spotlight August, 2023 Energy, Climate and Conservation, Grid policy-briefs energy climate-and-conservation grid 
Dividing Decarbonization by Sector: How Strategies for Decarbonizing Heat, Electricity, and Transportation Differ June, 2023 Decarbonization, Energy, Innovation and Technology policy-briefs decarbonization energy innovation-and-technology 
Unseen Threats to U.S. Infrastructure Reliability April, 2023 Damage Prevention, Energy, Innovation and Technology, Grid policy-briefs damage-prevention energy innovation-and-technology grid 
Unseen Threats to the U.S. Economy April, 2023 Damage Prevention, Energy, Economics policy-briefs damage-prevention energy economics 
Unseen Threats to the Environment April, 2023 Damage Prevention, Energy, Climate and Conservation policy-briefs damage-prevention energy climate-and-conservation 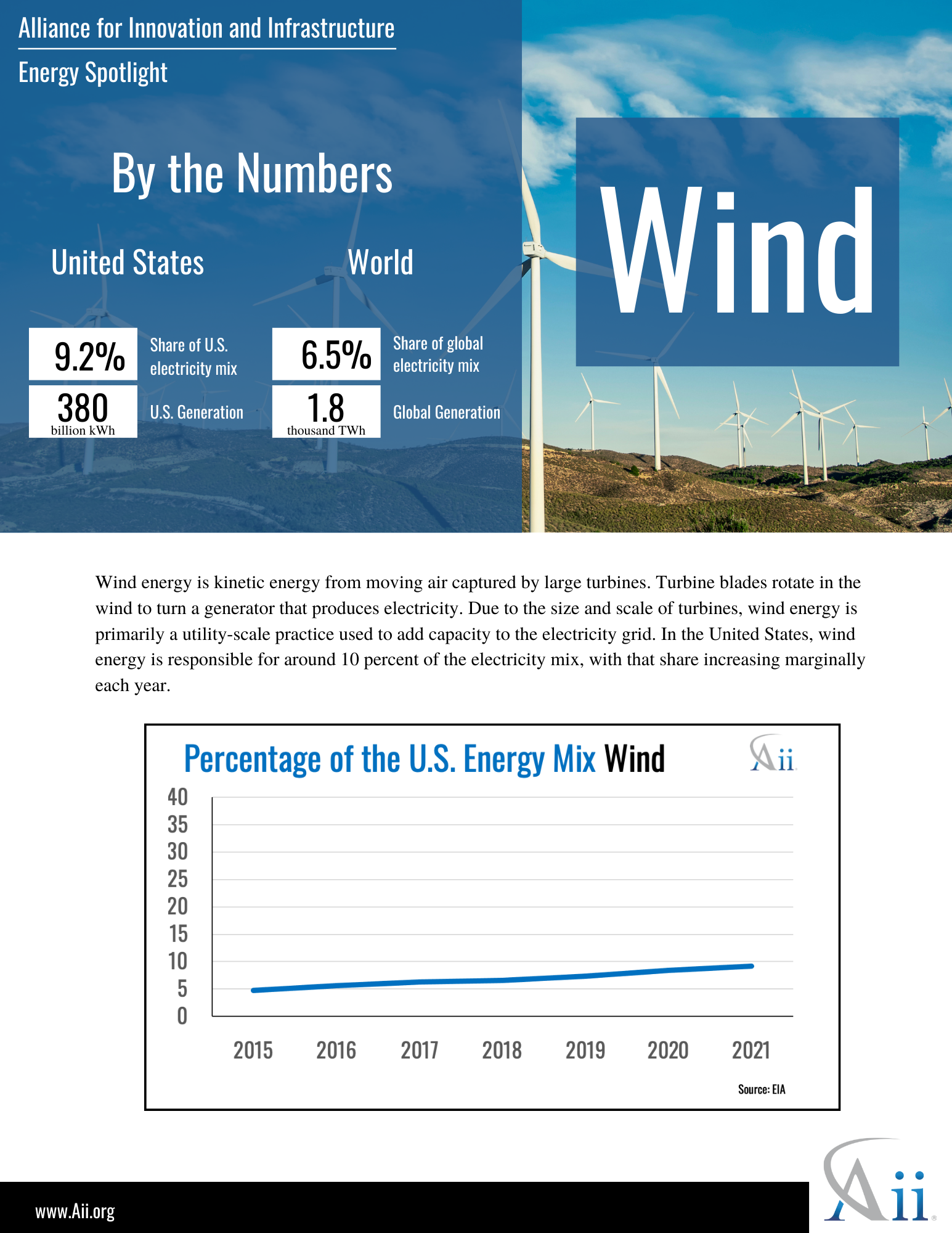
Energy Spotlight: Wind October, 2022 Energy, Climate and Conservation policy-briefs energy climate-and-conservation 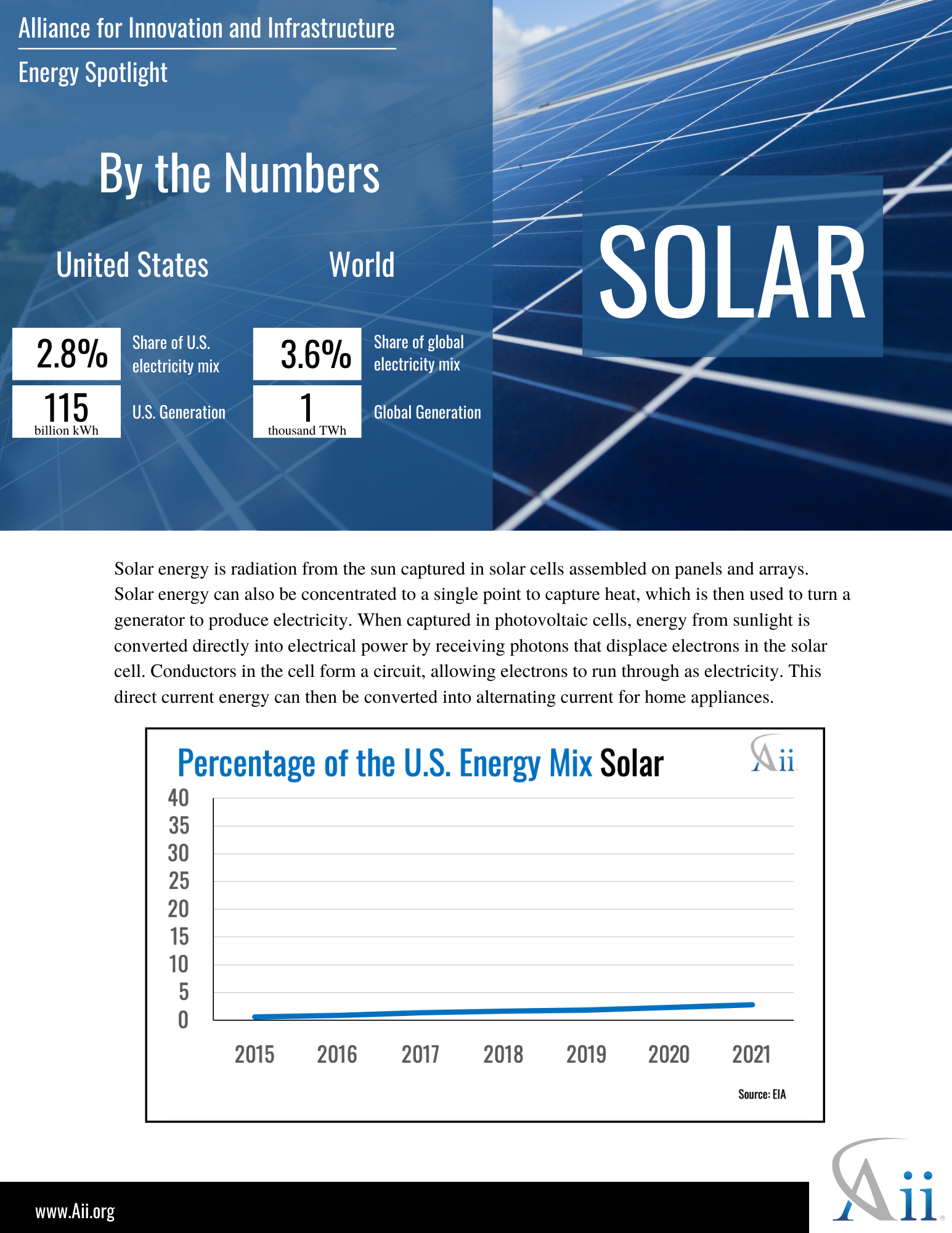
Energy Spotlight: Solar October, 2022 Energy, Climate and Conservation policy-briefs energy climate-and-conservation 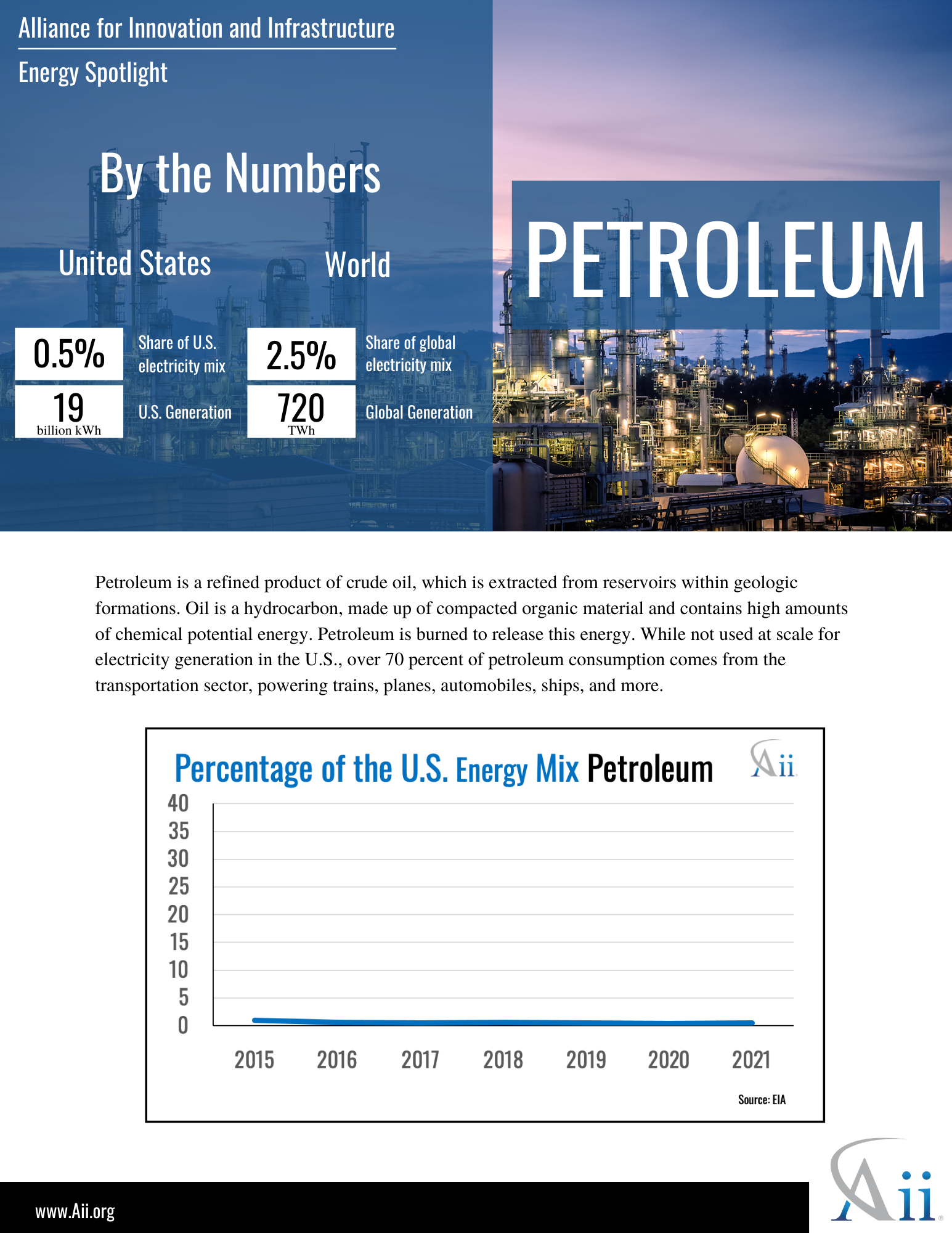
Energy Spotlight: Petroleum October, 2022 Energy, Climate and Conservation, Petroleum policy-briefs energy climate-and-conservation petroleum 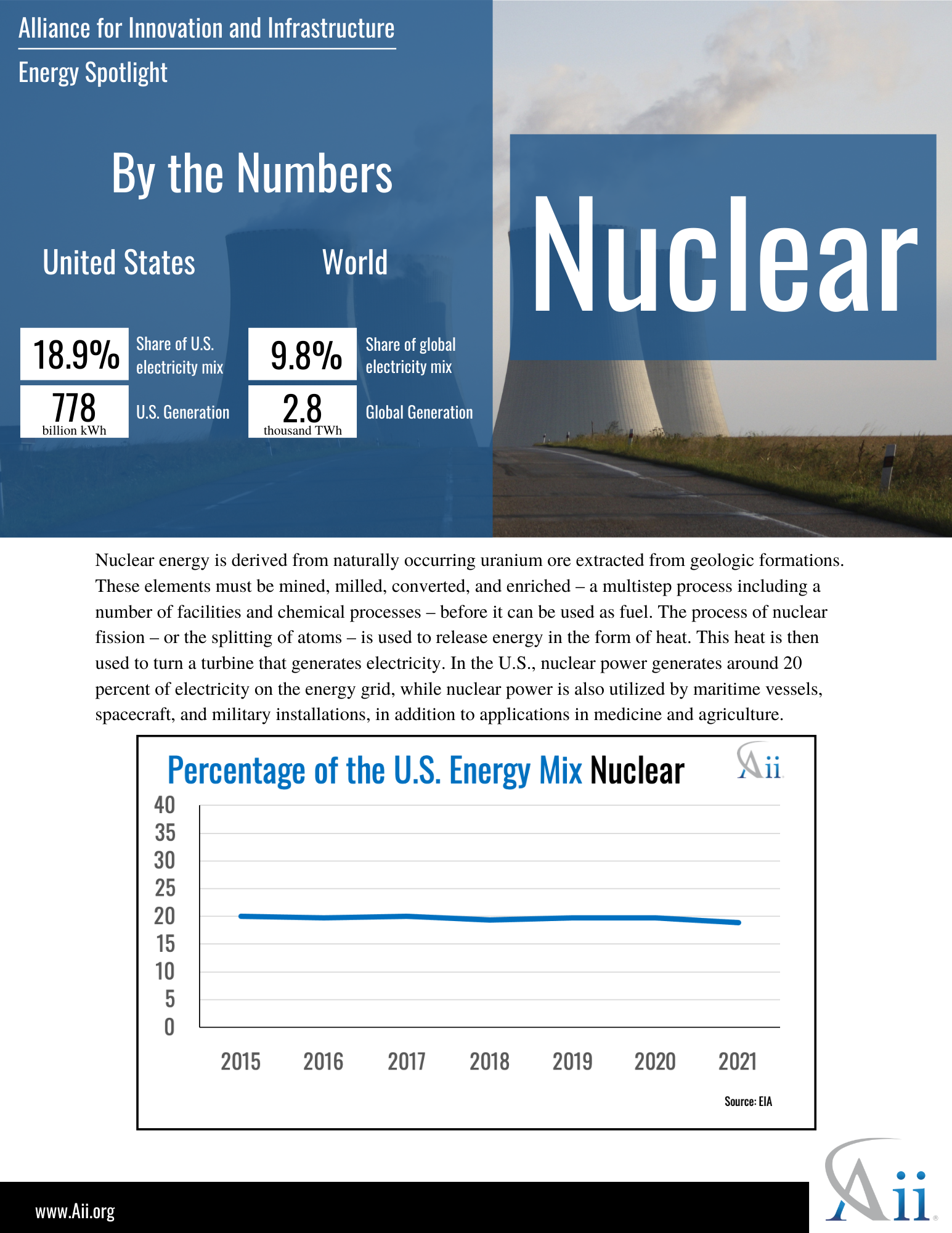
Energy Spotlight: Nuclear October, 2022 Energy, Climate and Conservation policy-briefs energy climate-and-conservation 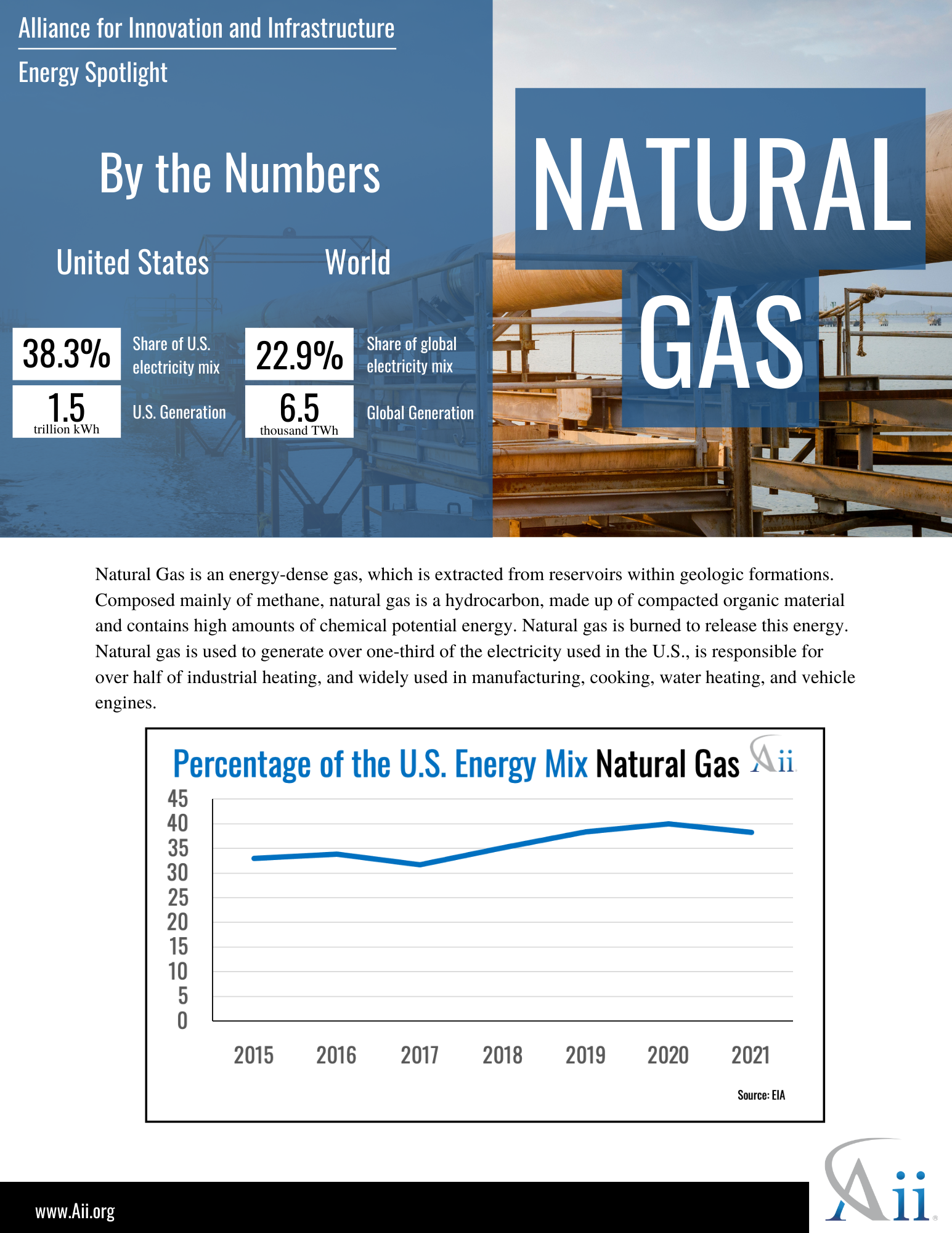
Energy Spotlight: Natural Gas October, 2022 Energy, Climate and Conservation policy-briefs energy climate-and-conservation 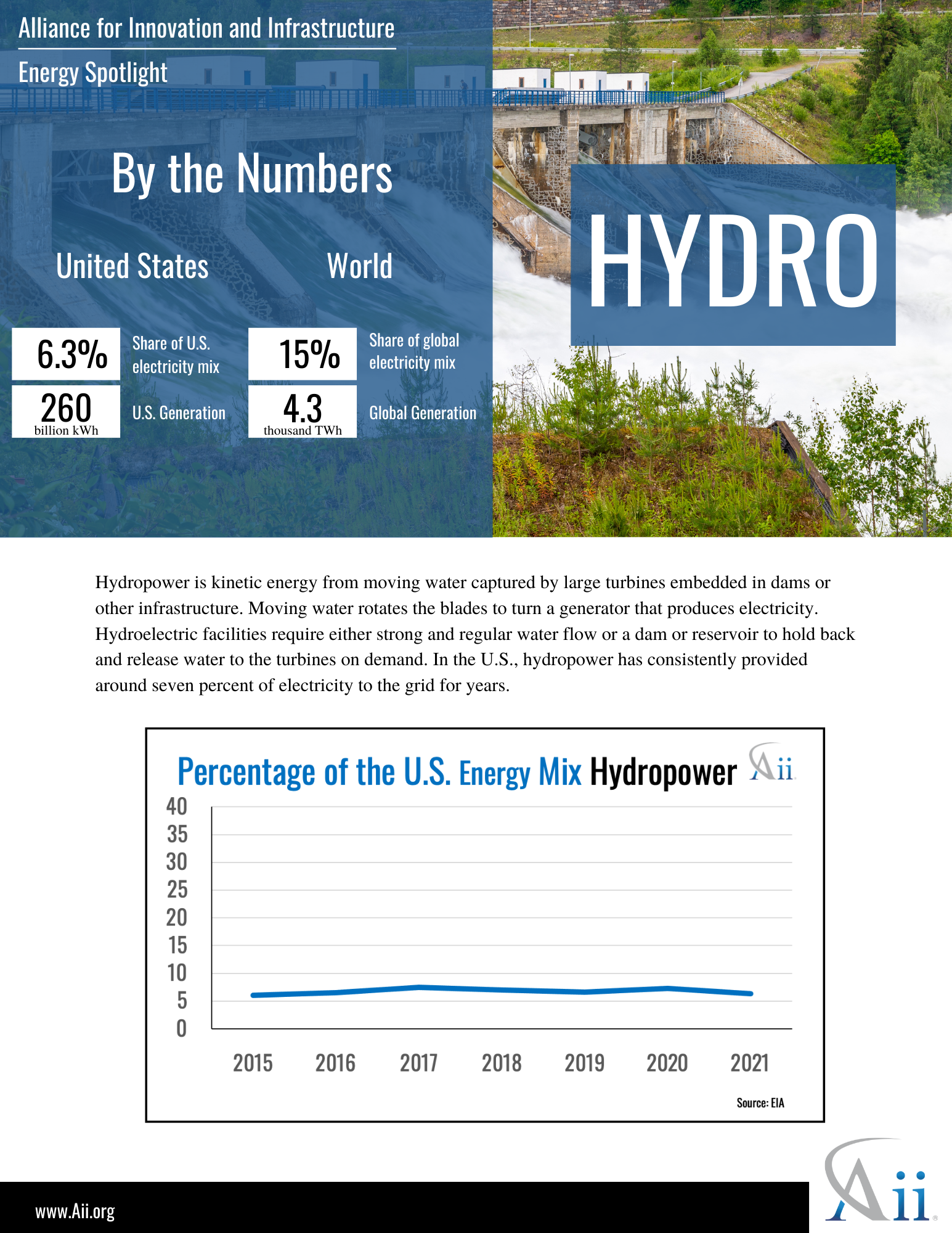
Energy Spotlight: Hydro October, 2022 Energy, Climate and Conservation policy-briefs energy climate-and-conservation 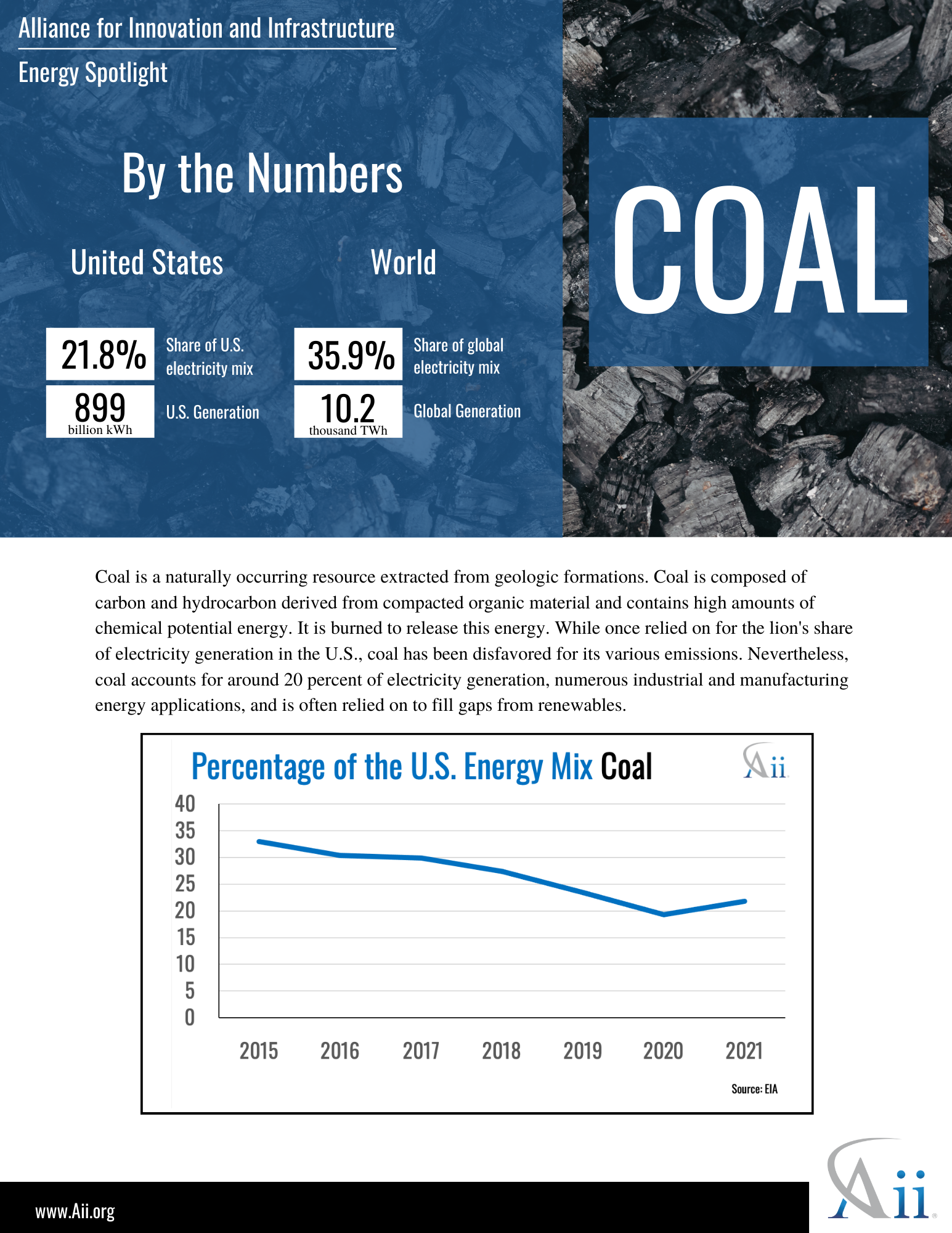
Energy Spotlight: Coal October, 2022 Energy, Climate and Conservation policy-briefs energy climate-and-conservation 
Federal Damage Prevention Overview April, 2022 Damage Prevention, Energy, Public Safety policy-briefs damage-prevention energy public-safety 
Excavation Damage to Underground Infrastructure: A Look at the Federal Damage Prevention Approach April, 2022 Damage Prevention, Energy, Public Safety white-papers damage-prevention energy public-safety 
A Sustainable Energy Model January, 2022 Energy, Innovation and Technology white-papers energy innovation-and-technology 
FEATURE: Ensuring Resilient Infrastructure and Climate Balance January, 2022 Energy, Public Safety white-papers energy public-safety 
ESG in the Oilfield December, 2021 Energy, Innovation and Technology, Public Safety white-papers energy innovation-and-technology public-safety 
Improving Upon Our Dig Laws: Evaluating an Anomalous Year, Incorporating Technology, and Applying Lessons from the Past Decade December, 2021 Damage Prevention, Energy, Innovation and Technology, Public Safety white-papers damage-prevention energy innovation-and-technology public-safety 
Petroleum Brief August, 2021 Energy, Climate and Conservation, Petroleum policy-briefs energy climate-and-conservation petroleum 
Solar Energy Brief August, 2021 Energy, Climate and Conservation policy-briefs energy climate-and-conservation 
Hydropower Brief August, 2021 Energy, Climate and Conservation policy-briefs energy climate-and-conservation 
Wind Energy Brief August, 2021 Energy, Climate and Conservation policy-briefs energy climate-and-conservation 
Coal Brief August, 2021 Energy, Climate and Conservation policy-briefs energy climate-and-conservation 
Nuclear Energy Brief August, 2021 Energy, Climate and Conservation policy-briefs energy climate-and-conservation 
Natural Gas Brief August, 2021 Energy, Climate and Conservation policy-briefs energy climate-and-conservation 
Building Back Better and Protecting What We’ve Built May, 2021 Damage Prevention, Energy, Innovation and Technology, Public Safety policy-briefs damage-prevention energy innovation-and-technology public-safety 
IMO 2020 Rule Primer: Background and Potential Impacts May, 2019 Energy, Climate and Conservation policy-briefs energy climate-and-conservation 
Best Practices to Achieve Excavation Safety September, 2018 Damage Prevention, Energy policy-briefs damage-prevention energy 
Challenges to Increasing Non-Federal Investment in Private Infrastructure: How Can the U.S. Turn $200B into $1.5T? March, 2018 Transportation, Energy, Innovation and Technology policy-briefs transportation energy innovation-and-technology 
Building a Smarter Electric Grid: How Investing In Smarter Electricity Will Energize America July, 2017 Energy, Innovation and Technology, Transmission, Grid white-papers energy innovation-and-technology transmission grid 
ARCTIC PROMISE: Challenges and Opportunities in Realizing the Next Generation of U.S. Arctic Infrastructure February, 2017 Transportation, Energy, Climate and Conservation, Petroleum white-papers transportation energy climate-and-conservation petroleum 
The Energy (Dis)Union: Challenges and Opportunities in the Emerging Market (ITALIAN) October, 2016 Energy, Innovation and Technology, Economics, Transmission, Grid white-papers energy innovation-and-technology economics transmission grid 
The Energy (Dis)Union: Challenges and Opportunities in the Emerging Market (POLISH) October, 2016 Energy, Innovation and Technology, Economics, Transmission, Grid white-papers energy innovation-and-technology economics transmission grid 
The Energy (Dis)Union: Challenges and Opportunities in the Emerging Market October, 2016 Energy, Innovation and Technology, Economics, Transmission, Grid white-papers energy innovation-and-technology economics transmission grid 
Infrastructure Resiliency: Preventing Damage Through Critical Investments July, 2016 Transportation, Energy, Innovation and Technology policy-briefs transportation energy innovation-and-technology 
Balancing Environmental Protection and National Infrastructure Development April, 2016 Transportation, Energy, Climate and Conservation policy-briefs transportation energy climate-and-conservation 
Aii Chairman Publishes Report in European Energy Journal March, 2016 Energy, Innovation and Technology, Economics white-papers energy innovation-and-technology economics 
Are P3’s a Practical Tool to Tackle the Growing Infrastructure Debt? February, 2016 Transportation, Energy, Innovation and Technology, Economics policy-briefs transportation energy innovation-and-technology economics 
Energy Storage December, 2015 Energy, Grid policy-briefs energy grid 
Can America Afford to Defund Rural Infrastructure? December, 2015 Transportation, Energy, Economics policy-briefs transportation energy economics 
Energy as an Instrument of Foreign Policy June, 2015 Energy, Innovation and Technology, Petroleum, Grid white-papers energy innovation-and-technology petroleum grid